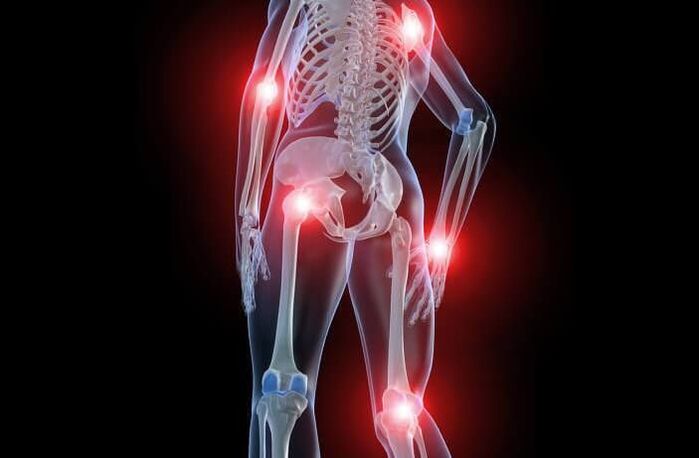
causes of joint pain
- New or old injuries.
- excess weight.
- High physical or sporting activity.
- Work involving standing for long periods of time.
- Passive lifestyle.
- age.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Weakened immune system.
- Infectious lesions of the body.
- Joints, Arthritis, Gout.
- Vasospasm during stress or overload.
Types of joint pain
| pain type | Occurrence conditions | describe | possible reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Occurs in people of any age during physical activity or exercise | With self-massage, physiotherapy procedures, pain will disappear while you rest | Changes in metabolic disorders, previous injuries, and dystrophy of articular cartilage tissue |
| start | Mark at the start of the movement | Severe pain and limited joint movement that subsides 3-5 minutes after starting physical activity | Arthropathy, osteochondrosis |
| night | intermittent pulling pain | Occurs during rest, during stress, overexertion, or after eating bacon or pickles | joints, gout |
| reflect | Twisting, aching, pulling pain | spread to surrounding tissues. Occurs during physical activity or when you are overweight | Spinal disease, joint disease, arthritis |
Doctor consultation and diagnosis
- chiropractor
- chiropractor
- Osteopath
- Neurologist
diagnostic tests
- blood test. By changing some indicators, the cause can be immediately identified;
- X-rays of the affected area. One of the most accessible and reliable studies;
- Synovial fluid sample. Thickening or changes in properties indicate changes in the joint;
- MRI. Provides layer-by-layer visualization of the tissue structure of the joint and its surrounding areas. Accuracy can be improved through comparison. Such diagnosis is mandatory when planning surgical intervention;
- ultrasound. Effective against inflammatory processes, systemic diseases, certain types of injuries;
- Scan both sides. The vascular environment of the organ and its blood flow quality can be assessed;
- CT. Creates a three-dimensional image of the organ under study, allowing assessment of function during movement.
Joint pain treatments
- Manual therapy. Manual correction of musculoskeletal problems. Return joints and bones to physiological position;
- physiotherapy. Utilizing natural and artificially created factors for effective treatment. Use light, water, magnetic or electric fields, temperature effects, etc. Painless surgery that activates the body’s own defenses;
- massage. Mechanical effects on subcutaneous receptors to relieve spasm and tension and optimize blood flow;
- Orthopedic shoes, insoles. Eliminate foot deformities, correct postural disorders, and relieve joints;
- Reflexology. Needles are inserted into biologically active points in the body. Improve microcirculation, blood pressure, and reduce pain;
- Ozone therapy. Fill tissues with oxygen, accelerate the regeneration of damaged organs, improve human immunity, and remove toxic damage;
- Plasma therapy. Injecting your own platelet-rich plasma can restore joints, skin and other organs;
- medical treatement. Pain syndrome can be relieved by taking painkillers. Cartilage protectors are used to rehabilitate affected joints. Can be injected into the lumen of a joint;
- Surgical treatment. Joints destroyed by disease are replaced by modern prostheses with the same functionality and considerable time resources. Suitable for severe disease cases.
Prevent joint pain
- Perform a series of specific exercises to support optimal joint function;
- go swimming;
- Avoid joint capsule overload and hypothermia;
- Control your weight and avoid being overweight;
- Drink 2-3 liters of water per day;
- Try to reduce alcohol consumption and quit smoking;
- Regular industrial exercise during daily sedentary or standing work;
- Provide timely and high-quality treatment of infectious and viral diseases. inflammatory diseases;
- Get regular annual physicals; if your joints show signs of discomfort, seek medical attention immediately.