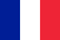
Arthropathy of the shoulder joint is a chronic disease caused by damage to cartilage tissue, followed by limited bone growth and movement. In most cases, the elderly suffer, but hard physical labor and inflammatory processes contribute to the early development of pathology. If left untreated, the movement of the affected joints will be completely blocked.
General information
Cartilage is the smooth layer between the contact areas of bones. It ensures that they slide easily relative to each other, guaranteeing free and painless joint work. Excessive stress, inflammation, or trauma can trigger a degenerative process that gradually spreads to the entire surface.
As a result, the smoothness of the articular surface is disturbed, and the movement starts to cause pain. At the same time, bone growth begins to appear at the edges of the joints, replacing the affected cartilage. As the degeneration process progresses, it involves not only the bones, but also the surrounding tissues. Limbs deformed, muscles cramped, ligaments weakened and lost their elasticity. Without treatment, patients will lose the ability to move their arms.
Times watched
According to the reasons for the development, primary and secondary arthropathy can be distinguished. The main form occurs alone, most commonly in the context of excessive joint overload. Secondary is caused by third-party pathology, such as trauma, severe inflammation, metabolic disorders, etc. The symptoms of these two diseases are similar.
the reason
Unlike the knee, ankle, and hip joints, the shoulder joint is not subject to significant pressure when walking, which is why this form of arthropathy occurs much less frequently. Pathology may be caused by the following reasons:
- Frequent excessive physical activity: weightlifting, professional sports, vibration;
- Congenital abnormalities of the shoulder joint structure and adjacent structures;
- Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases;
- Congenital connective tissue weakness, accompanied by joint hypermobility;
- Injuries: dislocation, sprain and ligament rupture, intra-articular fracture;
- Hormonal changes and disorders (including pregnancy, menopause);
- Inflammatory diseases of the joints and surrounding structures (arthritis, bursitis, etc. );
- Metabolic disorders, including gout and diabetes.
Heredity plays an important role in the susceptibility of joint disease.
Bachelor of Science
The doctor determines the 3 degrees of the deformed shoulder joint, which determines its symptoms and the choice of treatment strategies:
- Grade 1 performance is mild: the pain only appears when intense or prolonged exertion, and it disappears quickly after resting. X-rays show subchondral sclerosis of the articular surface;
- With secondary arthropathy, the pain becomes more intense, and a person must use analgesics to make them feel better; X-rays show that the joint space is significantly narrowed, cartilage destruction areas are large, and bone growth (osteophytes);
- Grade 3 is accompanied by persistent severe pain and obvious limitation of joint range of motion. The picture shows complete destruction of cartilage tissue, deformation of bone structure, and a large number of osteophytes.
symptom
The main symptoms of shoulder joint disease include:
- Pain: due to the loss of smoothness of the articular surface, osteophyte growth and bone deformation; the intensity, duration and nature of the sensation depend on the degree of injury;
- Crunch: one of the characteristic symptoms of the disease, appears in the early stage; the difference from the physiology lies in the coarser tone, which is often accompanied by pain;
- Restriction of movement: It is related to the appearance of pathological growth and damaged cartilage particles in the joints; in the first stage, it shows mild morning stiffness, and later it grows to be completely immobile (stiffness);
- Deformation: In the later stages of the disease, only the contours of the joints change first, and then the contours of the hands. This indicates that the cartilage is completely destroyed and bones, muscles and ligaments are involved in the pathological process.
It may take years or even decades for symptoms to progress, but eventually arthropathy of the shoulder joint can lead to inability to move the arm and severe pain.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of shoulder joint arthropathy requires a comprehensive approach. In order to accurately diagnose and determine the extent of the disease, doctors use the following methods:
- Inquiry and collection of medical records: record the main complaint of the patient and determine the occurrence of certain symptoms; undoubtedly, information about past illnesses and injuries, whether the parents have joint damage;
- Inspection: The doctor conducts a visual assessment of the joints to determine the range of motion and the area of greatest pain;
- X-ray and CT: The main diagnostic method allows you to see the characteristic symptoms of osteoarthritis (narrowing of the joint space, cartilage degradation, bone growth and deformity);
- Ultrasound: It can assess the condition of cartilage, bones, ligaments, joint capsules and muscles;
- MRI: allows you to obtain virtual slices of all structures in the affected area;
- Laboratory diagnosis: blood tests show an active inflammatory process, usually accompanied by arthropathy;
- Arthroscopy: Insert a camera through a small hole to examine the joint from the inside.
If the disease is secondary, the underlying pathology must be examined and consulted by narrow experts.
Shoulder arthropathy treatment
The treatment of shoulder joint arthropathy depends on the extent of the disease: in the first and second stages, the disease can be successfully stopped or delayed by the correct choice of drugs. For large areas of damage, the only way to restore mobility and completely stop the pain is surgery-arthroscopy to "clean" the joint.
medical treatement
The medical treatment of shoulder joint disease aims to relieve symptoms and restore cartilage tissue. For this, the following drug groups are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: block inflammation and relieve pain; available in the form of tablets, ointments, suppositories and injections;
- Hormonal drugs (corticosteroids): used when non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are ineffective and have similar effects; long-acting drugs injected directly into the joint cavity provide good results;
- Antispasmodic, B vitamins: used to reduce muscle spasms that inevitably accompany advanced arthropathy;
- Cartilage protective agent: designed for long-term use, aimed at repairing cartilage tissue;
- Drugs that improve microcirculation: indirectly stimulate the regeneration process by improving the blood supply to the affected area;
- Enzyme blockers: partially slow down the destruction of cartilage tissue.
The selection, dosage, dosing frequency and duration of specific drugs are only carried out by the doctor! It is important to remember that self-medication can cause accelerated joint degeneration and other side effects.
physiotherapy
Physical therapy techniques and physical therapy exercises greatly promote the progression of the disease and enhance the effects of drugs. The following procedures have been proven to have good results:
- Magnetic therapy: relieve pain, reduce inflammation, improve microcirculation, stimulate cartilage tissue regeneration;
- Shockwave therapy: exposure to sound waves of a specific frequency can help destroy osteophytes, thereby promoting movement of the affected joints;
- Electrophoresis, sound wave introduction: use electric pulses or ultrasound to introduce drugs (pain relievers, chondrprotectants) into tissues; promote better absorption of drugs;
- Massage and physiotherapy exercises: the dose load on the joints and violent manual movements stimulate blood circulation in the tissues.
Like medicine, physical therapy, massage, and exercise therapy should be prescribed and administered under the supervision of a specialist. If they are beneficial during quiet periods, their action in the context of the acute inflammatory process can lead to increased pain.
surgery
The final stage of shoulder arthropathy is accompanied by severe symptoms and requires surgical treatment. Most changes that occur due to degradation are irreversible, which is why the only way to restore a person’s mobility is endoprostheses. The affected joint was replaced with a modern prosthesis, which completely took over its function. This type of surgery is particularly effective for young and middle-aged people, because it allows you to live a painless life for many years.
prevention
Like any joint disease, shoulder arthropathy is easier to prevent than cure. The orthopedic doctor recommends the following rules:
- Eliminate or minimize professional risk factors (vibration, weightlifting);
- Don't let the physical strength decrease, and don't pursue sports records: It is best to choose a moderate training method;
- Control nutrition and weight;
- Check regularly to find out possible problems.
diet
For any degree of shoulder arthropathy, it is important to monitor nutrition:
- Avoid overeating and overweight;
- Minimize harmful products: fat, spicy, salty, alcohol, canned food, bacon;
- Eat enough foods rich in collagen (aspic, aspic) and omega-3 (fatty fish, olive oil);
- Prefer boiled, steamed or stewed foods over fried foods;
- Reduce the amount of fast-digested carbohydrates.
The diet should be complete, including the required amount of vitamins, minerals and nutrients.
Consequences and complications
Even slight shoulder pain and tightness can become unpleasant consequences. If left untreated, arthropathy can cause:
- Severe limitation of mobility until rigidity (bone fusion);
- Severe pain even when resting;
- The shoulders and the entire arm are severely deformed.
In order to avoid these problems, it is important not to search the Internet for how to use folk remedies to treat shoulder joint arthritis, but just contact an orthopedic surgeon to choose a treatment method.
Treatment in a specialist clinic
It is impossible to cure joint disease on your own. Experts in modern clinics provide patients with complex methods to treat shoulder joint disease:
- Combining modern drug treatments with high efficiency and minimal side effects;
- New and tried-and-tested physiotherapy techniques;
- PRP therapy;
- Physiotherapy exercises and massage to relieve limited joint movement.
If necessary, medical puncture of the joint is performed by introducing painkillers or artificial synovial fluid that promotes movement.
We monitor patients throughout the treatment process to control the disease.
Benefits of modern clinics
Professional blades provide their patients with:
- Comprehensive health check plan;
- Advanced inspection for accurate diagnosis;
- Consultation of various types of narrow experts;
- Modern treatment options include not only drugs, but also physical therapy, massage and exercise therapy;
- Reasonable prices for all services.
Shoulder joint disease is a problem that can completely change a person's life. Don't let the disease enter an irreversible stage, consult an orthopedic doctor.